In the realm of metallurgy, the art of forging has played a pivotal role in shaping materials for various applications. Among the most versatile and reliable options, steel forgings stand out as a testament to the marriage of strength and craftsmanship. Steel forgings, a process involving the shaping of metal through compressive forces, have found their place in numerous industries due to their inherent material properties and adaptability. Read More…
For over 30 years, we have provided metal forged products for a wide variety of industries, including the aerospace, military, food service, medical, and automotive industries. Our customers know they can trust our forgings for quality and affordability.
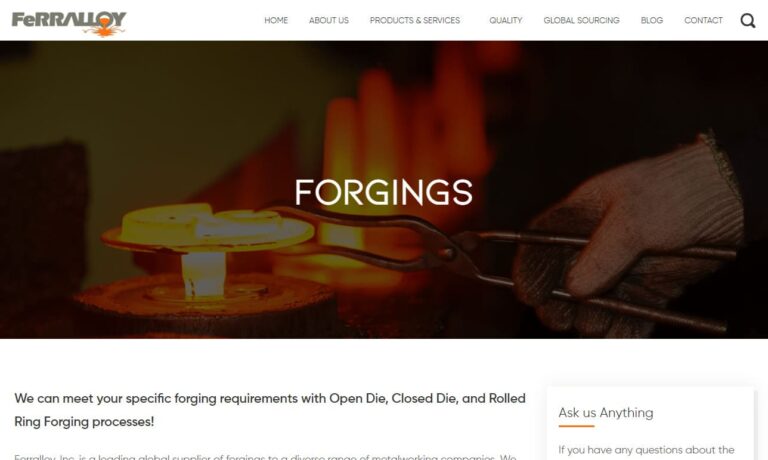
All Metals & Forge Group is your ISO9001:2015 and AS9100D registered forging facility. All Metals provides a wide range of materials, products and services, including discs, shafts, sleeves, cylinders, plates, blocks and many other shapes, both stock and custom, satisfying all of their customers’ requirements. Give All Metals & Forge Group a chance to satisfy your needs— you’ll be glad you...
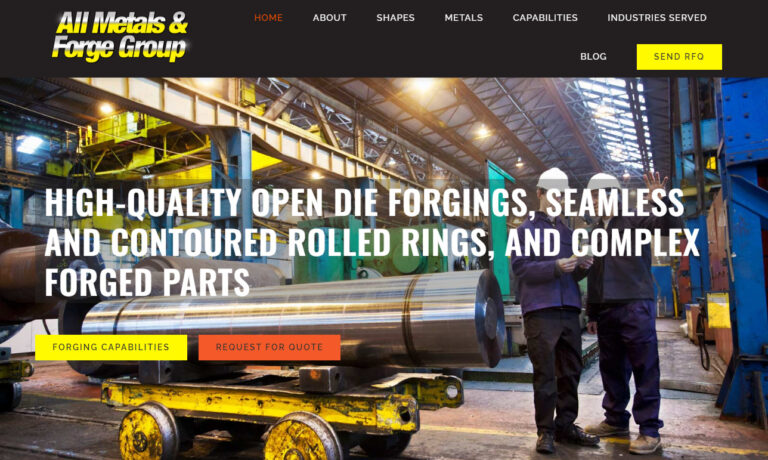
Although we have over 100 years of experience, we are committed to continually expanding our offerings in all industries. We are not content to remain as we are, but we continually work to improve our products and processes each and every day.
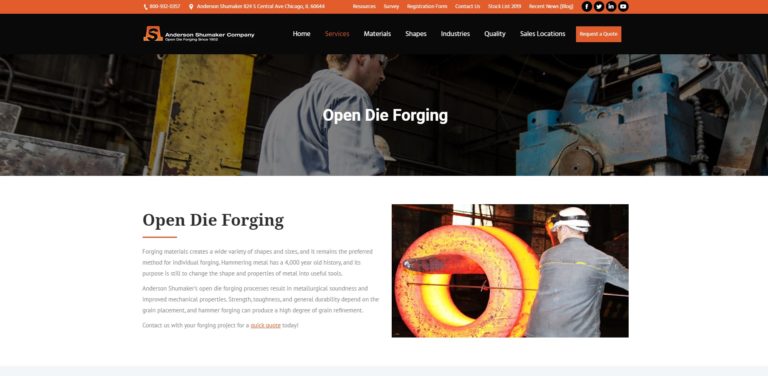
At Lenape Forged Products Corp., we take immense pride in our legacy of delivering high-quality forged products to a diverse array of industries. We specialize in producing precision-forged components that meet the rigorous standards required by our clients. Our extensive range of forgings includes everything from intricate custom parts to high-volume, standardized components, all meticulously...

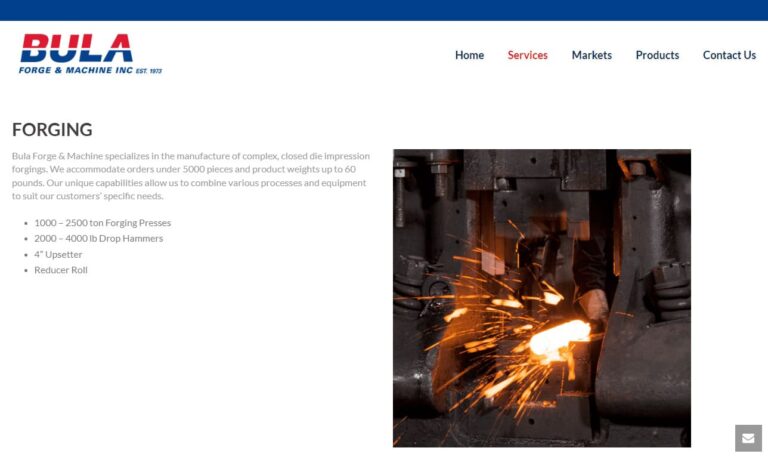
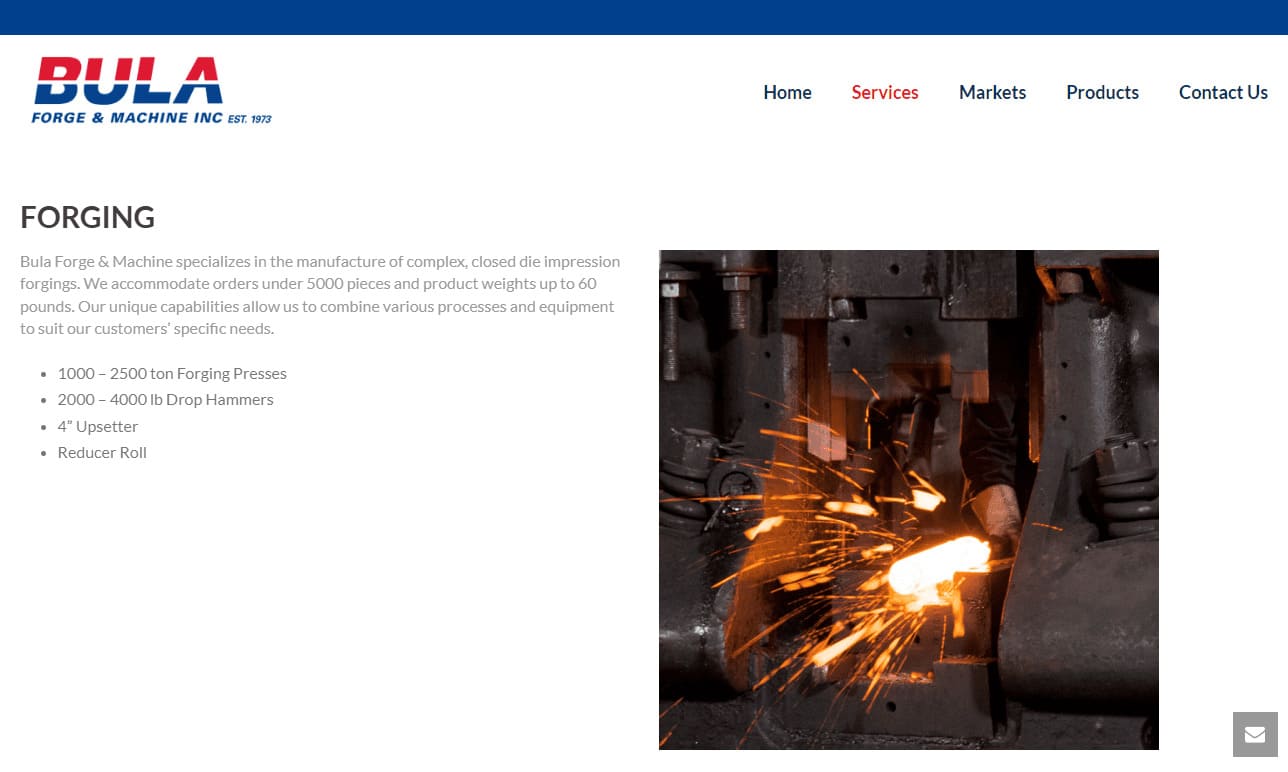
At Bula Forge & Machine, Inc., we are dedicated to delivering exceptional forging solutions that cater to a wide range of industries. Our expertise in the field of forgings is driven by a commitment to precision, innovation, and superior craftsmanship. We specialize in producing high-quality forged components that meet the rigorous demands of our clients.
More Steel Forging Companies
This article delves into the realm of steel forgings, exploring the grades, types of metals, applications, material properties, and a comparison with castings.
Grades of Steel Forgings
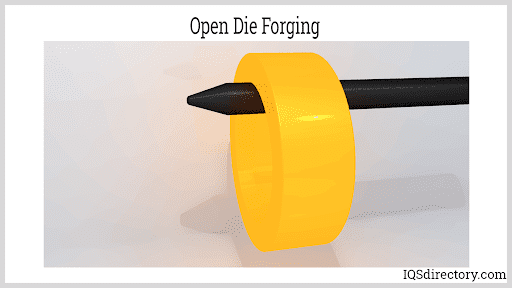
Steel forgings encompass a wide spectrum of grades, each tailored to specific purposes. These grades are categorized based on factors such as chemical composition, heat treatment, and mechanical properties. From low carbon to high alloy steels, the possibilities are vast. Low carbon steels offer ease of forging and high machinability, making them suitable for components that require intricate shaping. On the other hand, high alloy steels boast exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making them indispensable in heavy-duty applications.
Common Steel Forging Grade Systems:
AISI/SAE
The American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) jointly developed a system that categorizes steel forgings into various grades based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. This system aids in the identification of suitable forgings for applications ranging from automotive parts to industrial machinery.
ASTM
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has established an extensive classification system that covers a wide range of steel forging grades. These grades are designated by alphanumeric codes that provide information about the material's composition, mechanical properties, and heat treatment requirements. This system is widely used in industries such as construction, oil and gas, and aerospace.
DIN
The German Institute for Standardization (DIN) has devised a grading system known for its wide acceptance in Europe. This system classifies steel forgings based on various criteria, including chemical composition, mechanical properties, and heat treatment specifications. DIN grades are commonly used in applications requiring high precision and quality.
JIS
The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) system defines standards for steel forgings in Japan. These standards categorize forgings based on their composition, properties, and applications. The JIS system is significant not only in Japan but also internationally, especially in industries that value precision engineering.
Metals that Can Be Forged
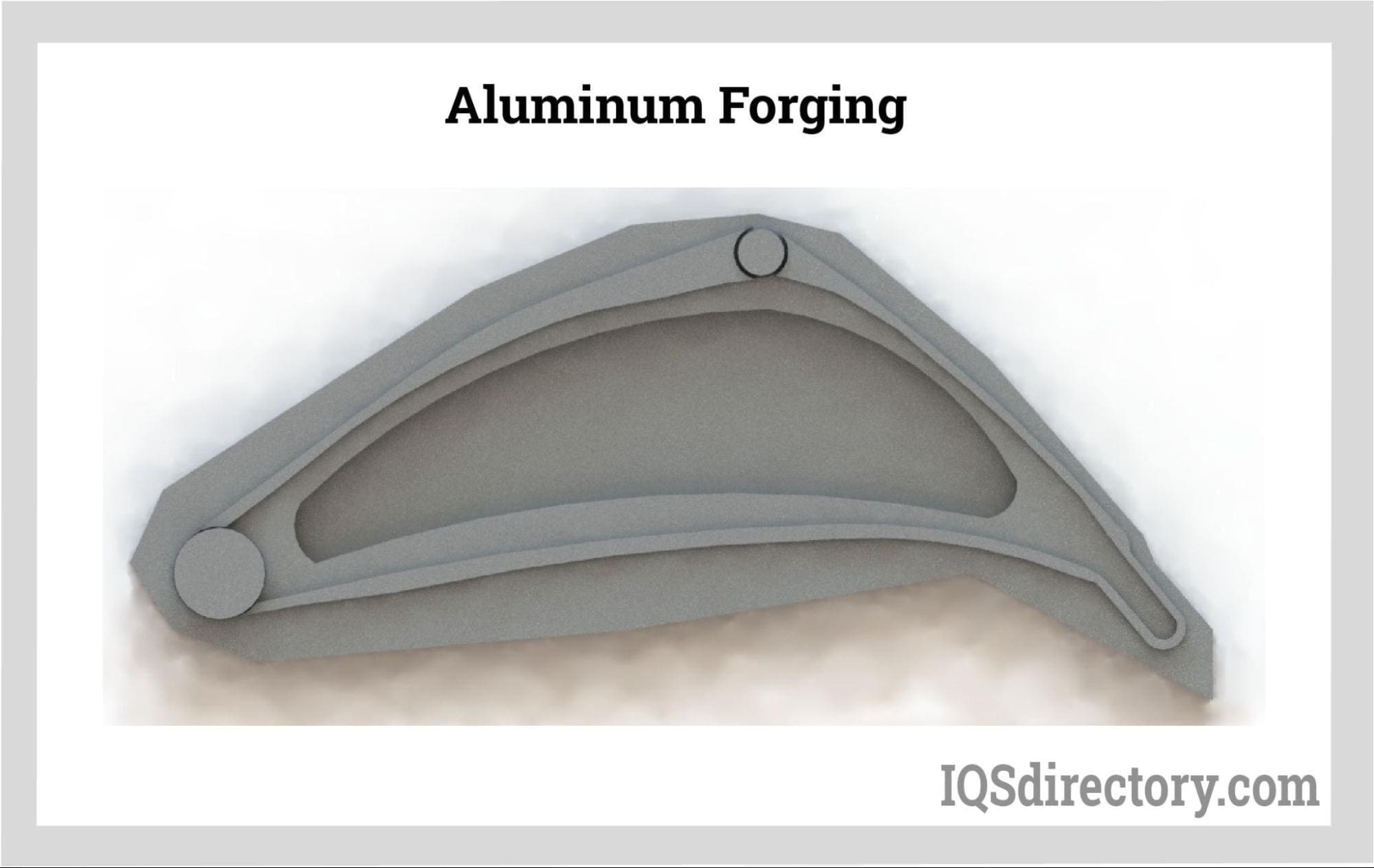
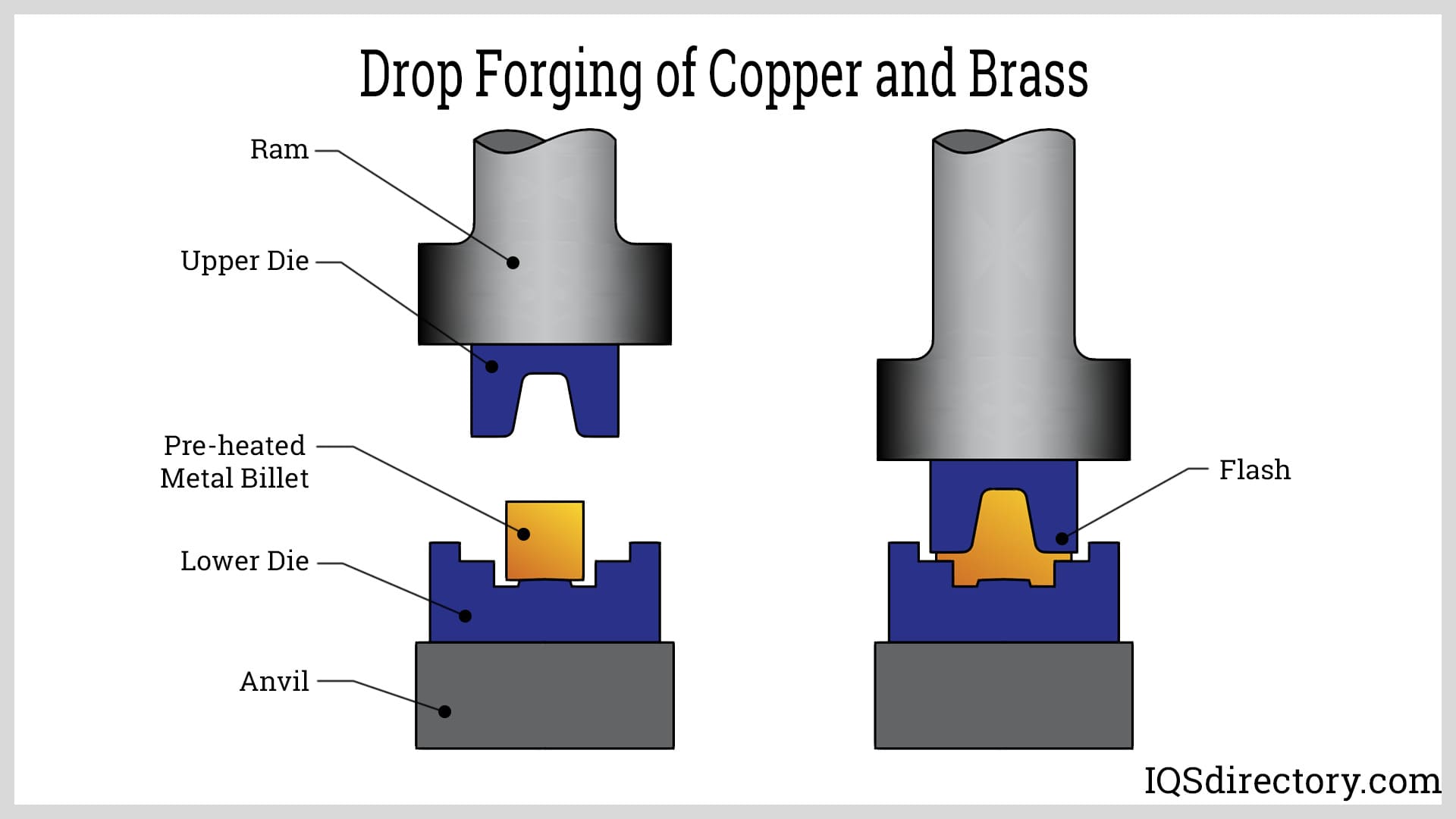
While steel is the most prominent material for forging, other metals can also be shaped using this method. Alloy metals, stainless steel, titanium, and even certain non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper can undergo the forging process. This versatility enables manufacturers to create components with diverse properties to meet specific needs.
Metals that Can't Be Forged
Despite the versatility of forging, there are metals that are less amenable to the process due to their inherent properties. For instance, brittle metals like cast iron and some high-carbon steels are challenging to forge due to their susceptibility to cracking under the intense pressure applied during the forging process. Additionally, some non-metallic materials like ceramics and plastics cannot be forged due to their lack of malleability.
Best Types of Steel for Forging
Certain types of steel are better suited for forging due to their composition and behavior under heat and pressure. Carbon steels and alloy steels are commonly preferred for forging due to their malleability and ability to maintain their structural integrity throughout the process. These steels can be heated to a plastic state, allowing skilled artisans to shape them with precision and care.
Applications of Steel Forgings
Steel forgings, widely recognized for their remarkable mechanical properties and enduring durability, exhibit their capabilities across a diverse spectrum of industries. Their influence catalyzes innovation and elevates performance standards across various sectors. Let us explore the extensive and impactful applications of steel forgings, which encompass fields ranging from aerospace engineering to power generation.
-
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, where safety and reliability are paramount, steel forgings play a critical role. Components like turbine disks, landing gear, and structural elements are subject to extreme temperatures, pressures, and stresses. High-strength steel forgings provide the necessary robustness to withstand these harsh conditions, ensuring the integrity of aircraft and propulsion systems.
-
Automotive Sector
The automotive industry benefits greatly from the precision and strength of steel forgings. Crankshafts, connecting rods, and suspension components demand high strength-to-weight ratios and fatigue resistance to withstand the rigors of daily use. Forged steel's enhanced material properties contribute to improved performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity of vehicles.
-
Oil and Gas Exploration
The oil and gas sector relies on steel forgings for critical equipment subjected to corrosive environments and extreme pressures. Components like wellhead fittings, valves, and drilling tools require exceptional durability and resistance to wear and tear. Steel forgings offer the necessary strength and reliability to withstand the challenging conditions of oil and gas exploration and extraction.
-
Power Generation
Steel forgings form the backbone of power generation infrastructure. In hydroelectric power plants, components like turbine shafts and blades endure high-speed rotations and hydraulic forces. In thermal power plants, pressure vessels, steam turbine rotors, and generator shafts demand materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures over long operational lifetimes.
-
Construction Industry
The construction sector benefits from steel forgings in various structural elements. Cranes, bridges, and high-rise buildings require steel components with exceptional load-bearing capabilities. Steel forgings provide the necessary strength and reliability to ensure the structural integrity of these projects.
-
Mining and Heavy Machinery
In the mining industry, equipment like drill bits, gears, and conveyor systems must endure abrasive materials and heavy loads. Steel forgings deliver the toughness and wear resistance required to sustain operations in demanding mining environments. Similarly, heavy machinery across industries, such as earth-moving equipment and industrial machinery, relies on steel forgings for their durability and longevity.
-
Defense and Military Applications
The defense sector leverages the strength and precision of steel forgings for critical applications. Armored vehicles, artillery systems, and naval components demand materials that can withstand ballistic impacts and extreme conditions. Steel forgings provide the necessary robustness to ensure the effectiveness and safety of defense systems.
Material Properties of Steel Forgings
The material properties of steel forgings are a result of both the forging process and the choice of steel grade. These properties include enhanced strength, fatigue resistance, and impact toughness. Due to the inherent grain refinement achieved during forging, steel forgings typically exhibit greater structural integrity than their cast counterparts. This refined grain structure contributes to improved mechanical properties, making them highly desirable for critical applications.
Steel Forgings vs Castings
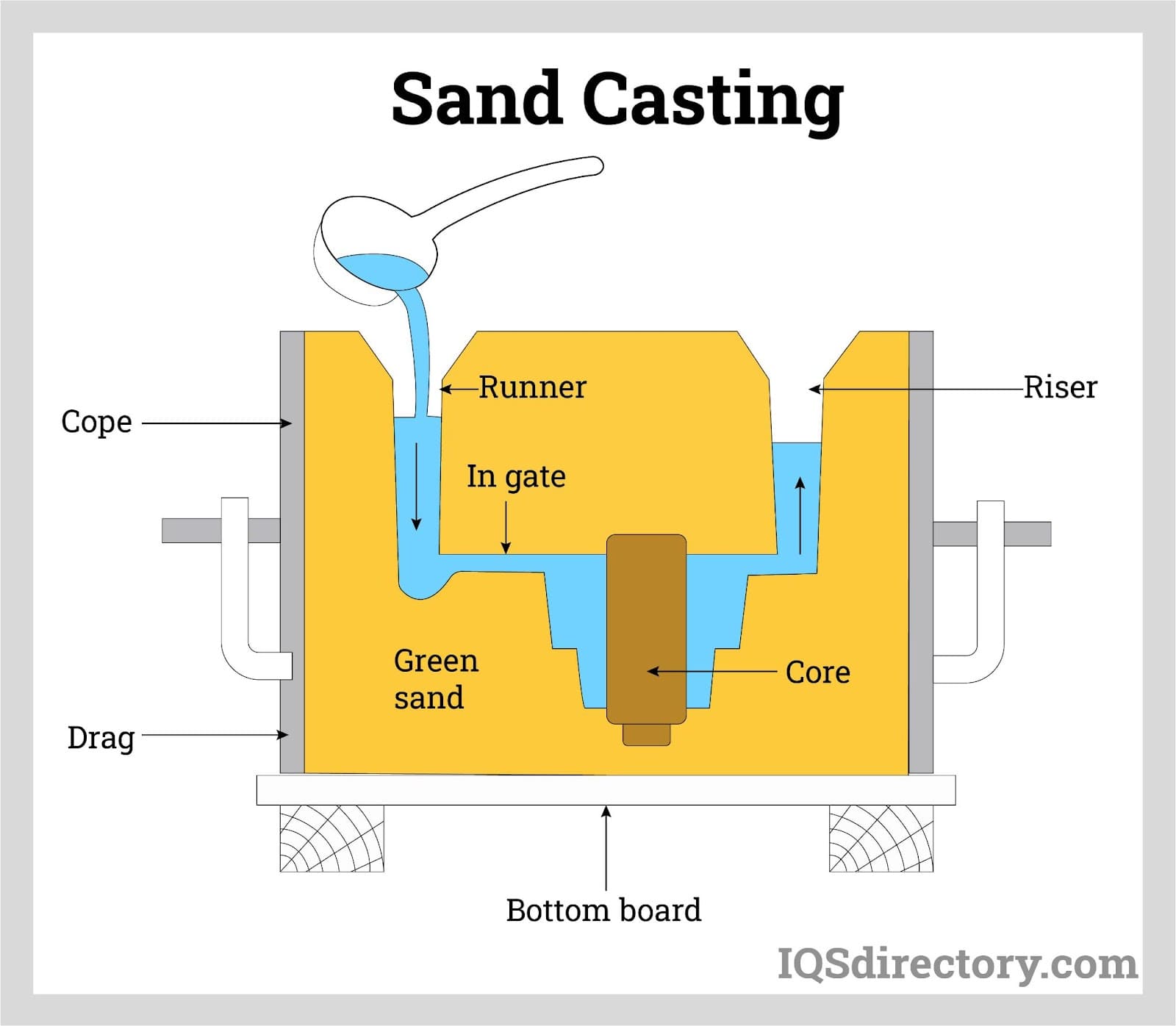
In comparison to castings, steel forgings possess several advantages. The forging process imparts directional grain flow, which results in superior mechanical properties such as increased strength and reduced porosity. Castings, on the other hand, can suffer from internal defects and irregularities in grain structure. Furthermore, the forging process enhances material consistency, resulting in components that have uniform properties throughout. This consistency is often challenging to achieve in castings due to the cooling and solidification process.







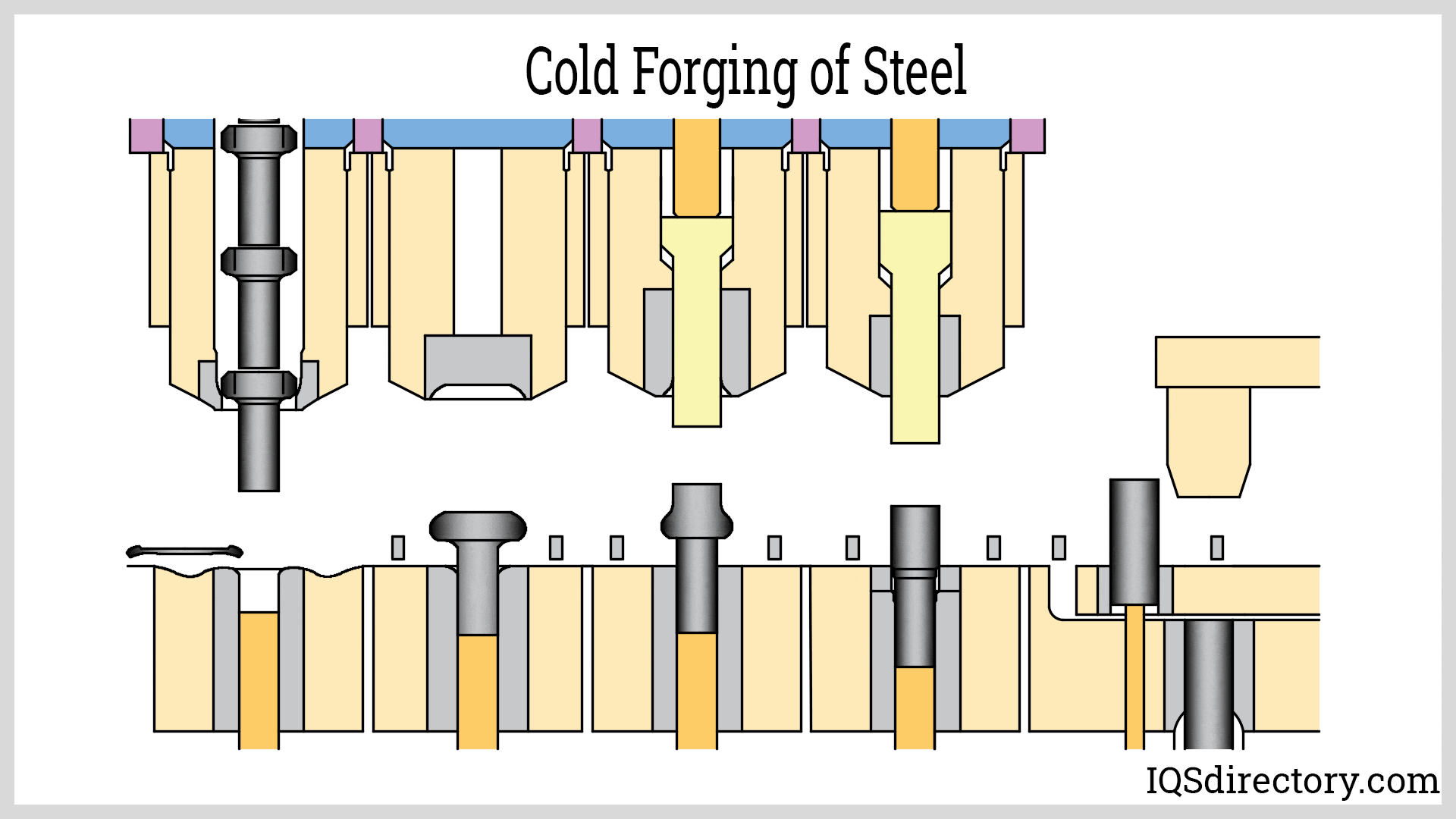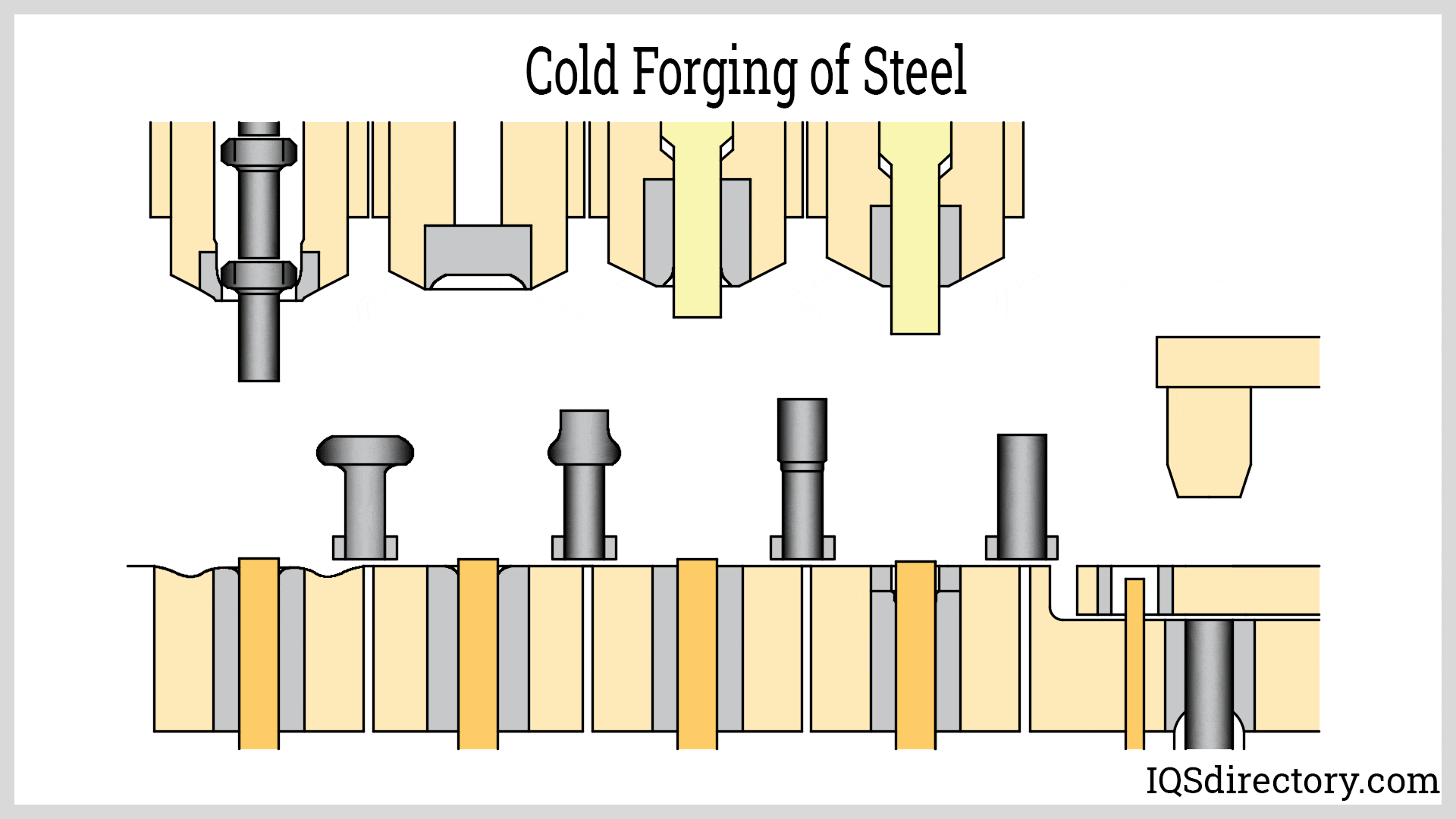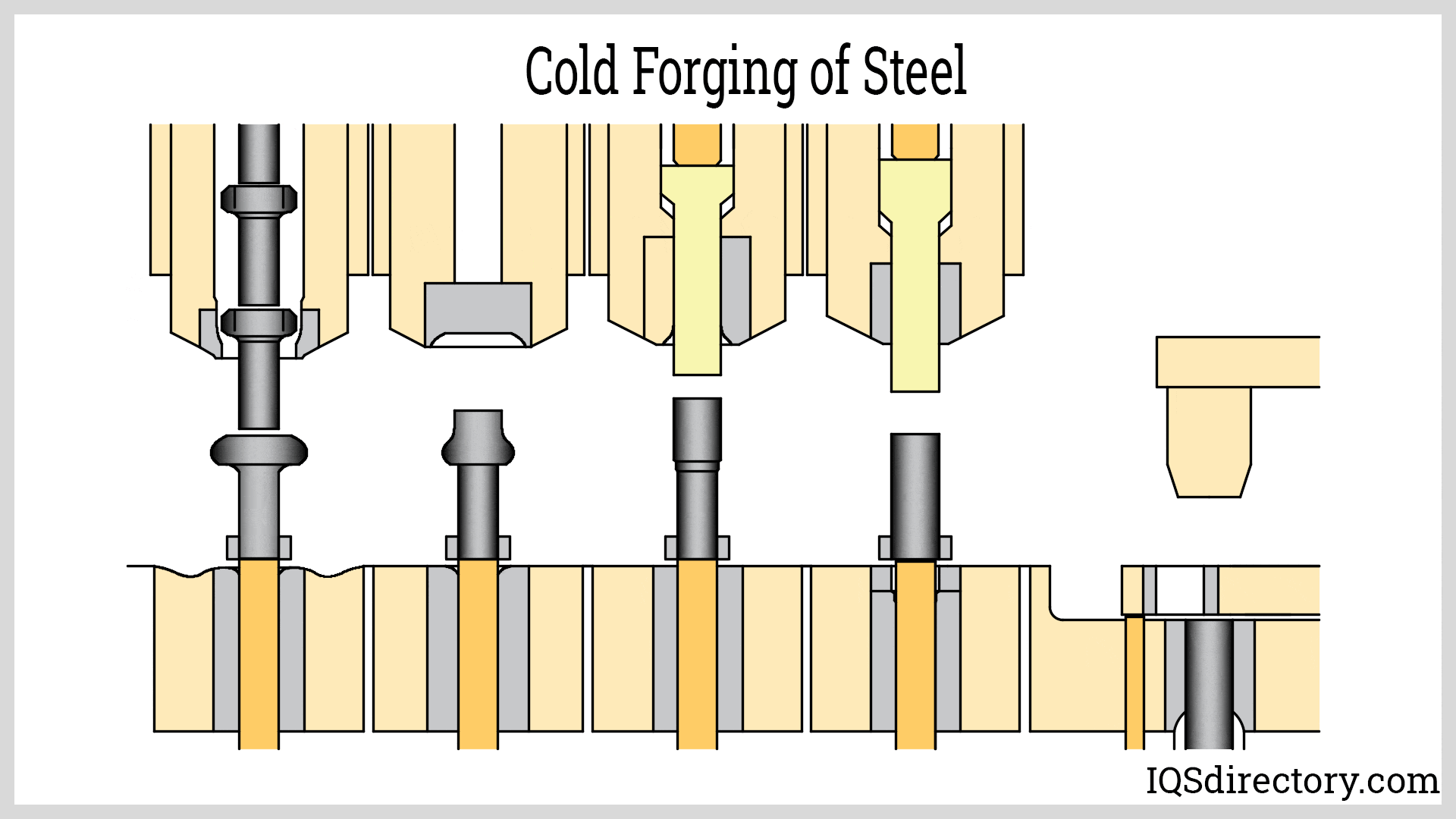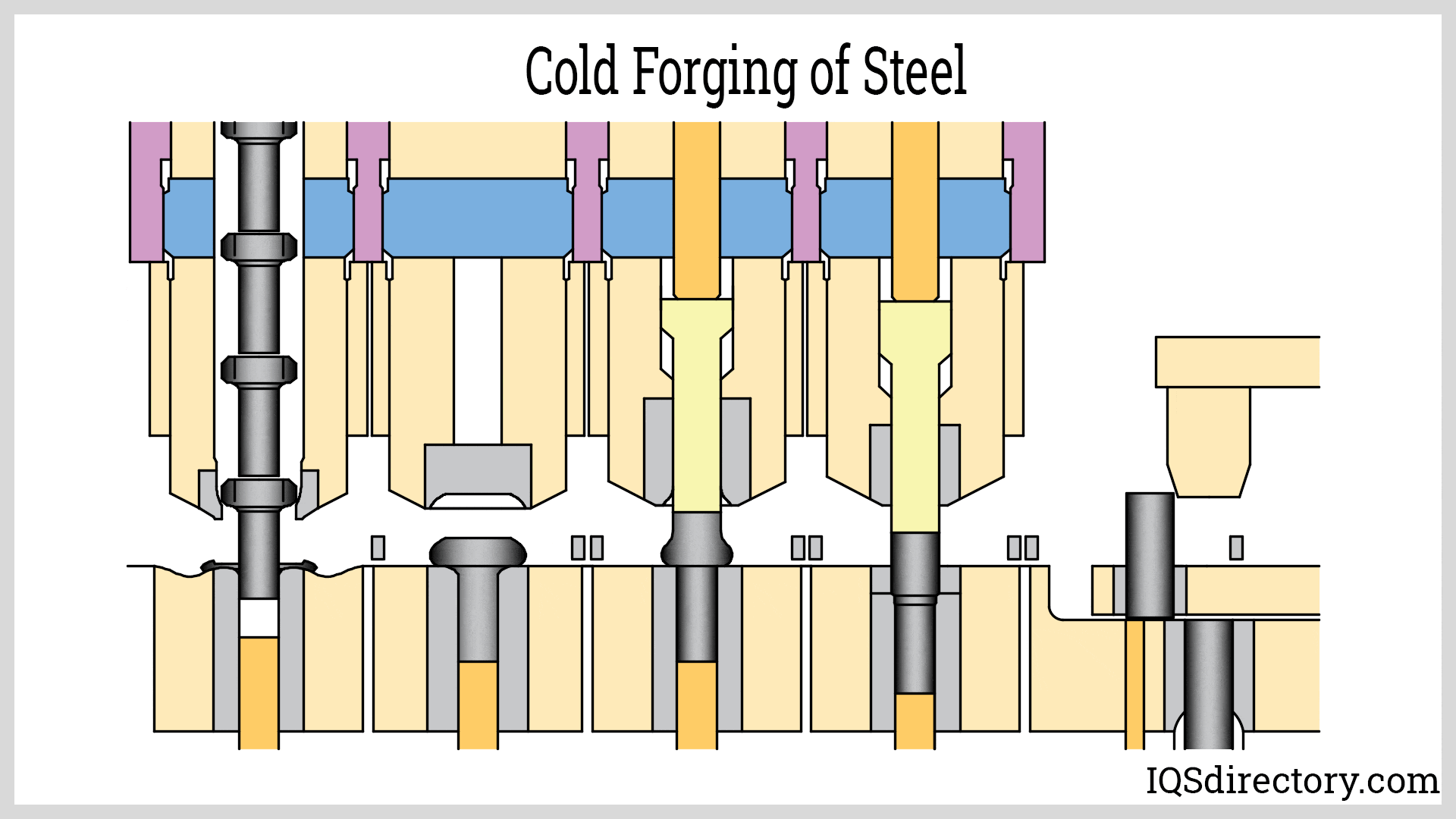
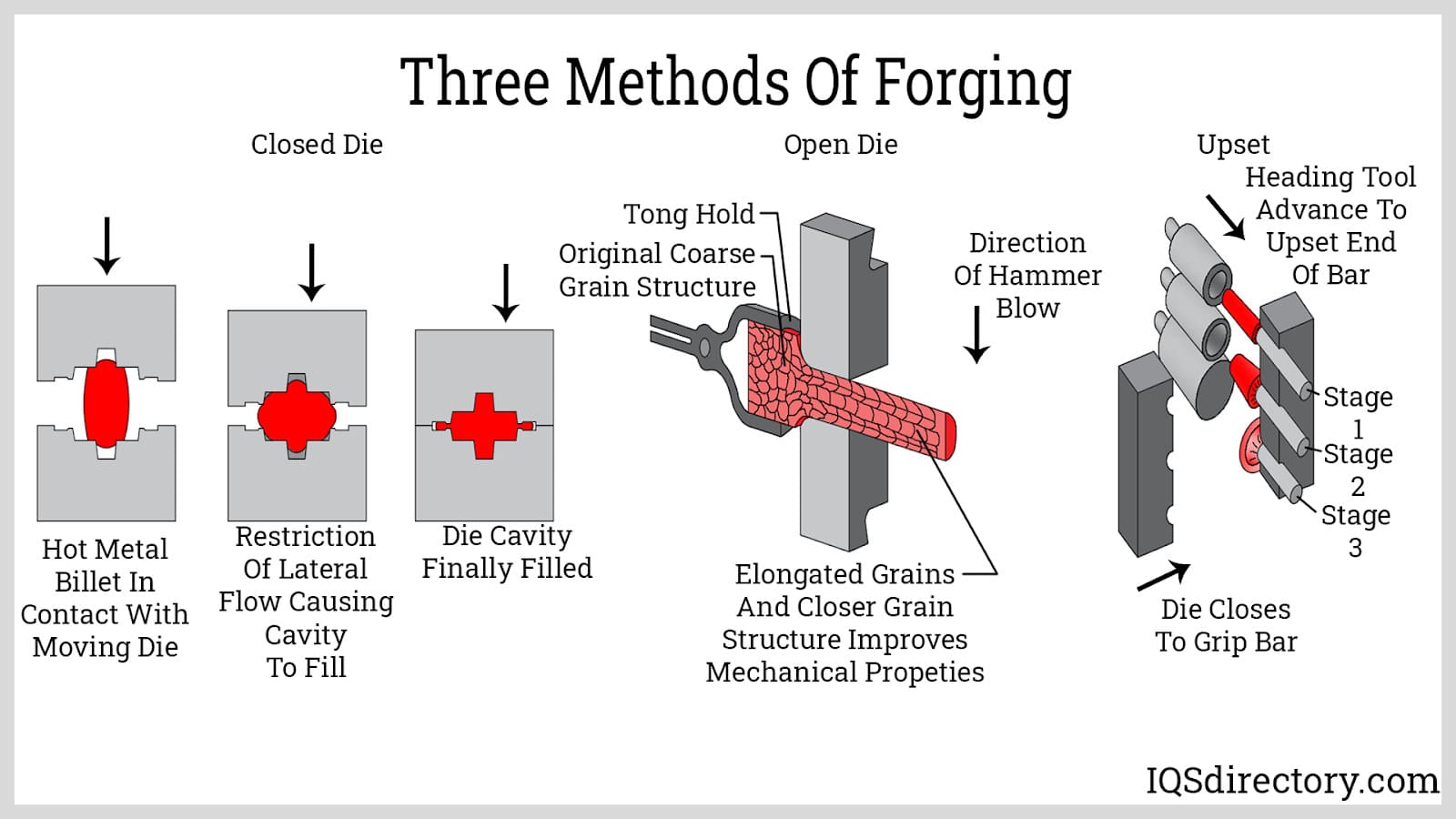
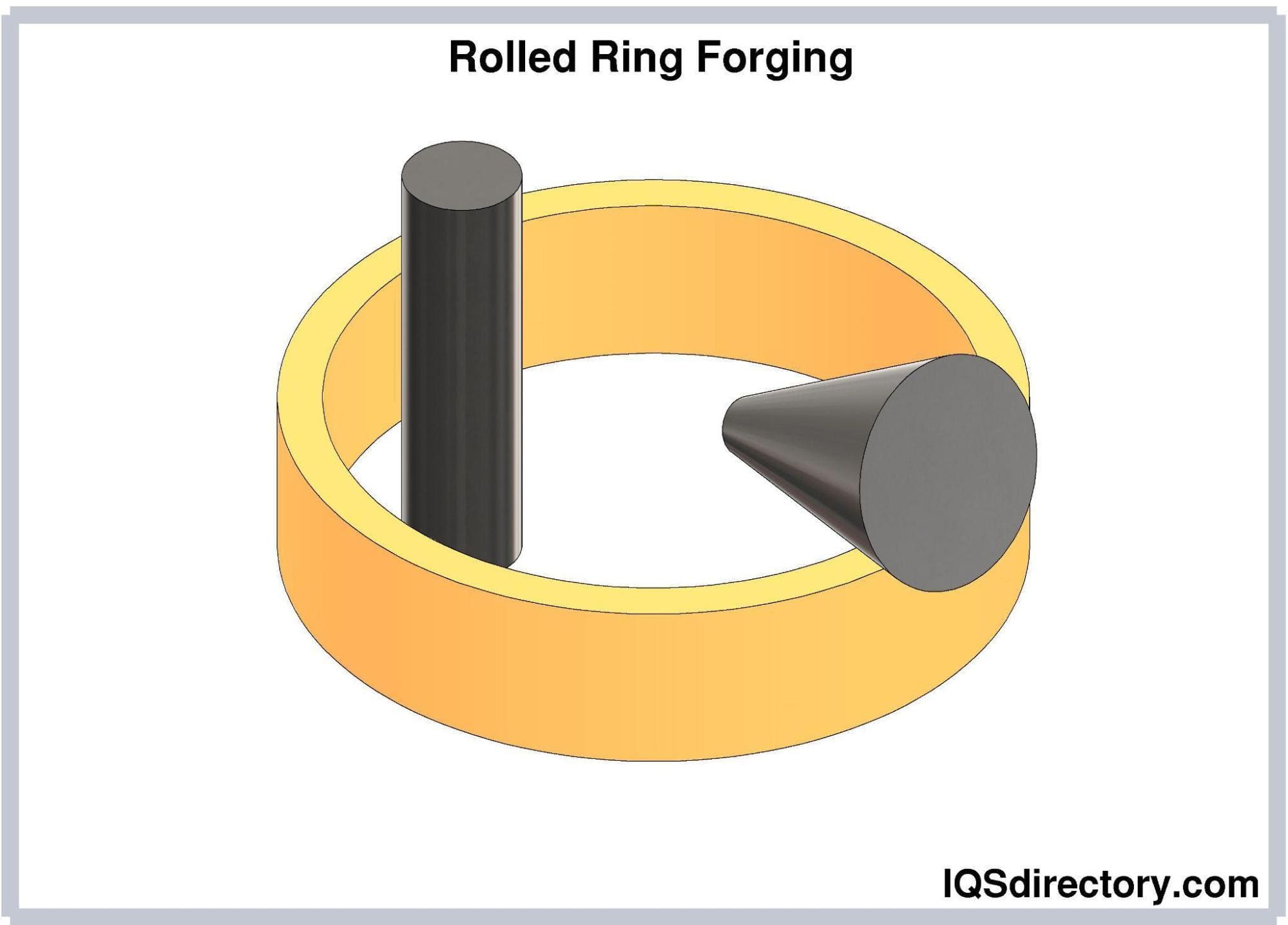
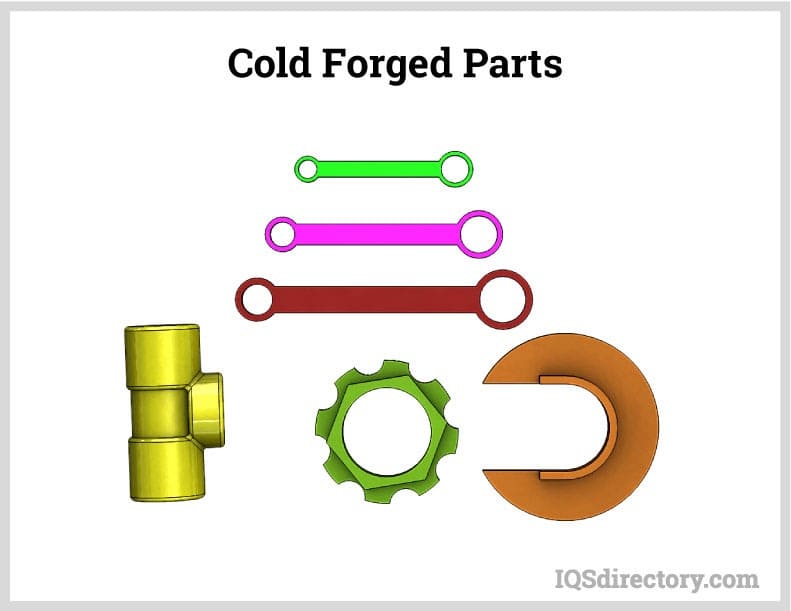

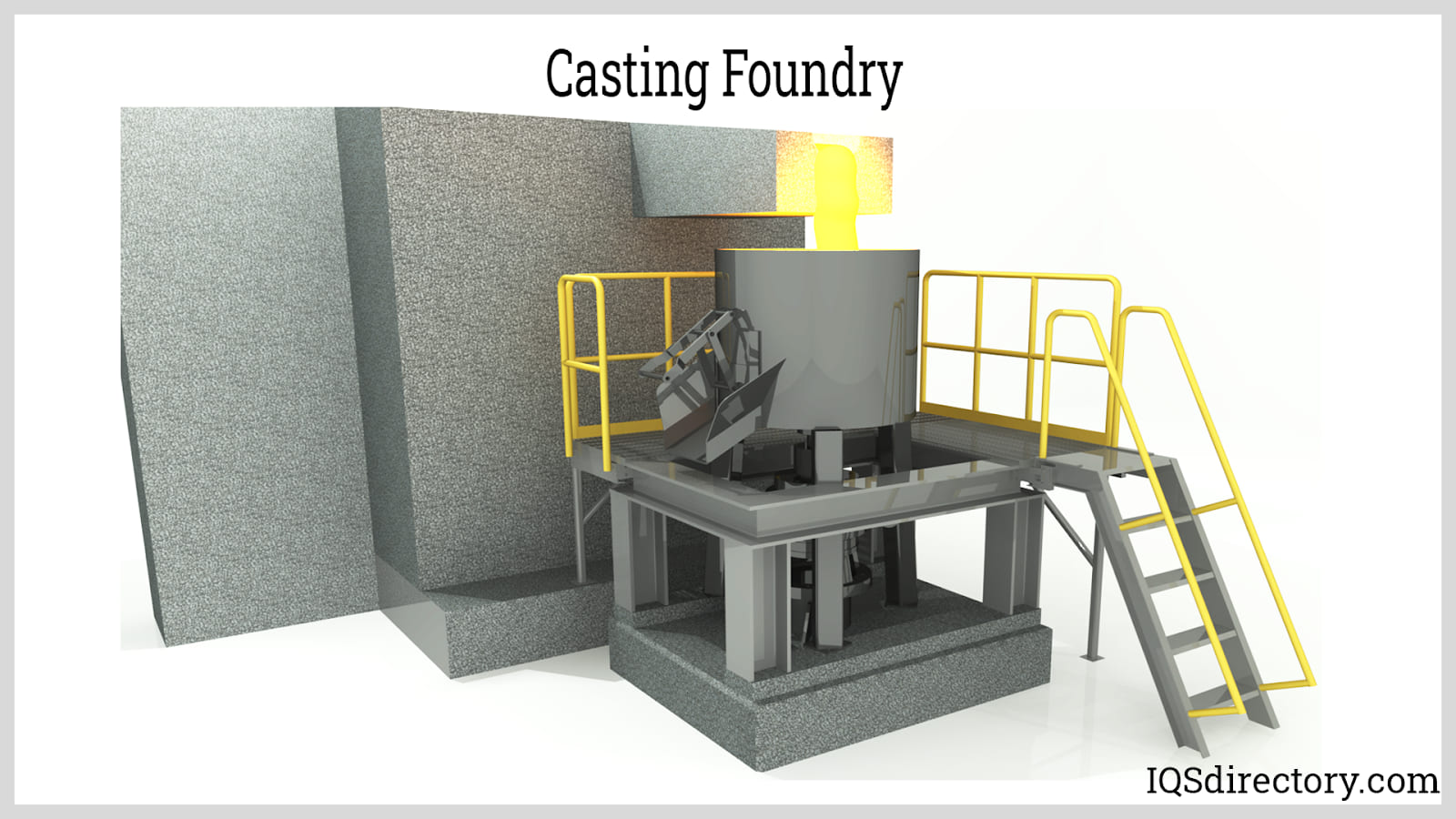
 Die Castings
Die Castings Forgings
Forgings Grey Iron Castings
Grey Iron Castings Investment Castings
Investment Castings Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services